An Introduction to Handshake Domains
As of October 2022 there are over 7 Million Handshake domains registered
Handshake (HNS) is a decentralized peer-to-peer network domain naming protocol that is aiming to fundamentally change the internet’s domain naming system landscape. Using blockchain technology (similar to cryptocurrency tech), handshake domains bypass the traditional centralized domain naming system overseen by ICANN. Critics of the current system argue that a centralized naming system is by its nature “vulnerable to hacking, censorship, and corruption.”
Handshake calls it an “experiment” to explore new ways in which to build a more decentralized internet. Essentially, the idea is that a decentralized system offers domain owners more security, privacy, freedom, and control over their domain name.
It is a naming protocol that’s backwards compatible with the existing DNS system. It does not replace the DNS protocol, but instead decentralizes the root zone file where TLD ownership information is stored by adding a distributed and decentralized blockchain-based system that no one controls and anyone can use. This allows for a root zone that is uncensorable, permissionless, and free of gatekeepers i.e ICANN etc.

How does Handshake work?
Handshake names can be virtually anything, from English letters and decimal numbers to Chinese characters and even emojis! They can be used like a traditional TLD with a subdomain (my.home/, my.家/, my.?/) or as a standalone name (home/, 家/, ?/).
Handshake has an auction based marketplace where anyone can bid on an available name. The person with the highest bid gets to own the name. In this scenario, everyone in the marketplace can transparently see the bidding activity on the platform.
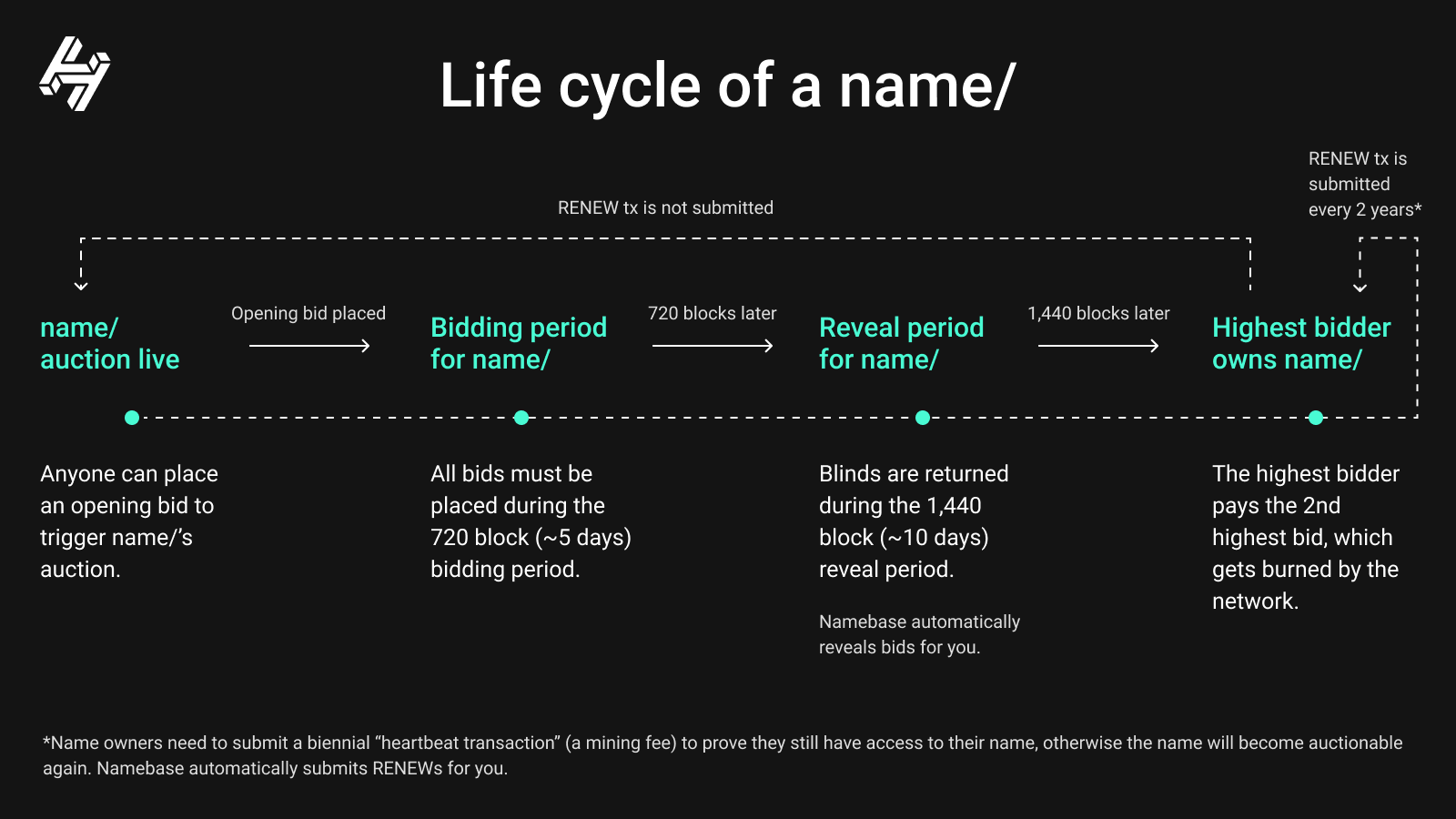
Handshake auctions are Vickrey-style auctions, which is a type of sealed-bid auction. Bidders submit their bids without knowing the bid of the other people in the auction. The highest bidder wins but the price paid is the second-highest bid. For example, if you bid 10 HNS for nakamoto/ and someone else bids 5 HNS, you’d win the auction and only pay 5 HNS for nakamoto/. This means that you don’t spend more HNS than you need to when you win an auction. The auction process is explained above and takes about 5 business days to complete. Domain names are renewed every 2 years.
Does Handshake replace DNS?
No. Handshake is meant to replace the root zone file, not DNS. The root is the dot (.) before the com. Browsing the web with human-readable names is how the Internet works. Handshake is not revolutionising domain names, but rather evolving them. Their solution allows for a seamless transition between a centralised name root zone file controlled by private parties to a decentralised root zone file controlled by actual Internet users. The Handshake blockchain itself is essentially one big distributed zone file in which anyone has the right to add an entry in.
Replacing CAs
Handshake names are their own root of trust and have their TLS keys pinned to themselves. Rather than relying on an arbitrary centralized list of hundreds of certificate authorities to verify public key authenticity, Handshake makes it possible for anyone to verify key authenticity by shifting the root of trust to a cryptographically backed distributed root of trust: its blockchain. Unlike with traditional domains where it takes but a single bad certificate authority to compromise your security, with Handshake it would require the entire Handshake blockchain to be compromised.
Handshake Pros

Full Autonomy and control over the domain names you register. You can create your own subdomain and web3 ecosystem.

The cost of owning your own generally Handshake domain name is under $100 depending on the auction result. In comparison to own your ICANN TLD was $185,000 to just apply.
Handshake Cons

The Vickery auction model means that brands need to compete with the general public for their own brand. We have seen auctions where brands are scuttled by bidders at the last minute and lose the rights to their namesake in Handshake domains.

Liquidity and Tech Problems: There have been recent issues with a hot wallet that has seen auctions fail or stall. There have also been issues with not enough liquidity meaning the blockchain itself can not operate. This is a red flag for the survivability of the program.
Handshake Brand Protection Program
Handshake held a ninety day sunrise period before launch to allow existing rights-holders to claim their trademarked names. This was in order to help the seamless transition from a centralized root zone file to a decentralized root zone file.
Existing TLDs and over 100,000 Alexa websites are reserved on the Handshake blockchain. Upon removing collisions, generic, and exclusions (e.g. 1 or 2 character names), approximately 80,000 names remain. Using the root key and DNSSEC, domain owners can cryptographically prove ownership to the Handshake blockchain to claim names. 100,000 was chosen as a number which the ownership is clear and has already gone through policy and process.
Brand Protection Options for Handshake
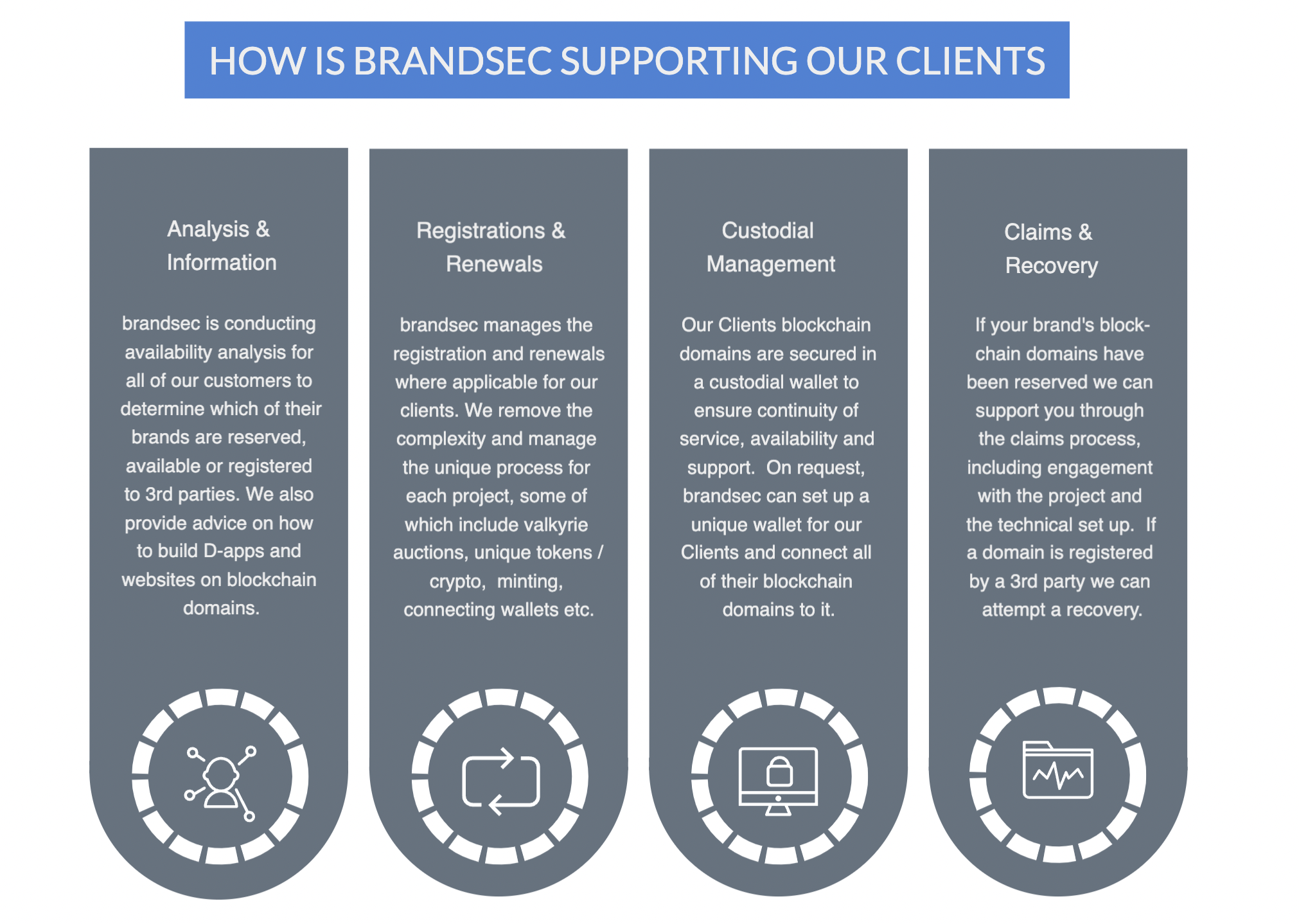
Defensive Registrations: The first step is to register your brand and products in the major blockchain projects. In some cases, you will find that your brand is reserved and can be claimed for free. If your brand is not reserved and available, we recommend registering it as soon as possible to prevent 3rd parties from squatting on it.
No Dispute Mechanism: The growing popularity of blockchain domains has seen a landrush of people registering their stake(s) in the new internet. Unlike traditional domains, there is no dispute mechanism such as the UDRP. The owner of a blockchain domain name is not likely to publicise its identity. Therefore, it is often impossible to ascertain their identity. This presents challenges in determining the proper party, jurisdiction, and venue with respect to anti-cybersquatting, infringement, or other legal claims.
Buying on OpenSea: We are seeing many branded domain names for sale on NFT marketplaces, especially OpenSea. Brandsec can negotiate on our client’s behalf to acquire domain names for a fee for service, which includes defining a budget, communication strategy and purchase management.
Dispute Notice to Marketplaces: Trademark owners cal also send takedown notices to the marketplaces selling infringing .eth domains. OpenSea, Rarible, and Nifty Gateway all have procedures in place (with varying degrees of effectiveness) to deal with intellectual property violations. Once a takedown notice is sent to OpenSea, for example, OpenSea will notify the owner of the domain that the listing has been removed due to a takedown request (meaning it’s no longer for sale to the public). The notice will allow the owner to contact the brand holder, which might spawn more reasonable negotiations since the domain has been delisted. This approach could result in a more permanent remedy.
Other Blockchain Domain Name Projects
Our